Insider Brief
- The global market for industrial robot installations reached a record $16.7 billion, driven by labor shortages, rising operational complexity, and demand for more flexible automation, according to the International Federation of Robotics.
- The IFR identifies accelerating adoption of AI-driven autonomy, IT/OT convergence, and early industrial deployments of humanoid robots as key forces reshaping how robots are designed, deployed, and evaluated for reliability, efficiency, and scalability through 2026.
- Growing safety, cybersecurity, and liability concerns, alongside persistent workforce gaps, are pushing manufacturers to pair automation with stronger governance frameworks and workforce upskilling as robots take on a larger role across industrial and service environments.
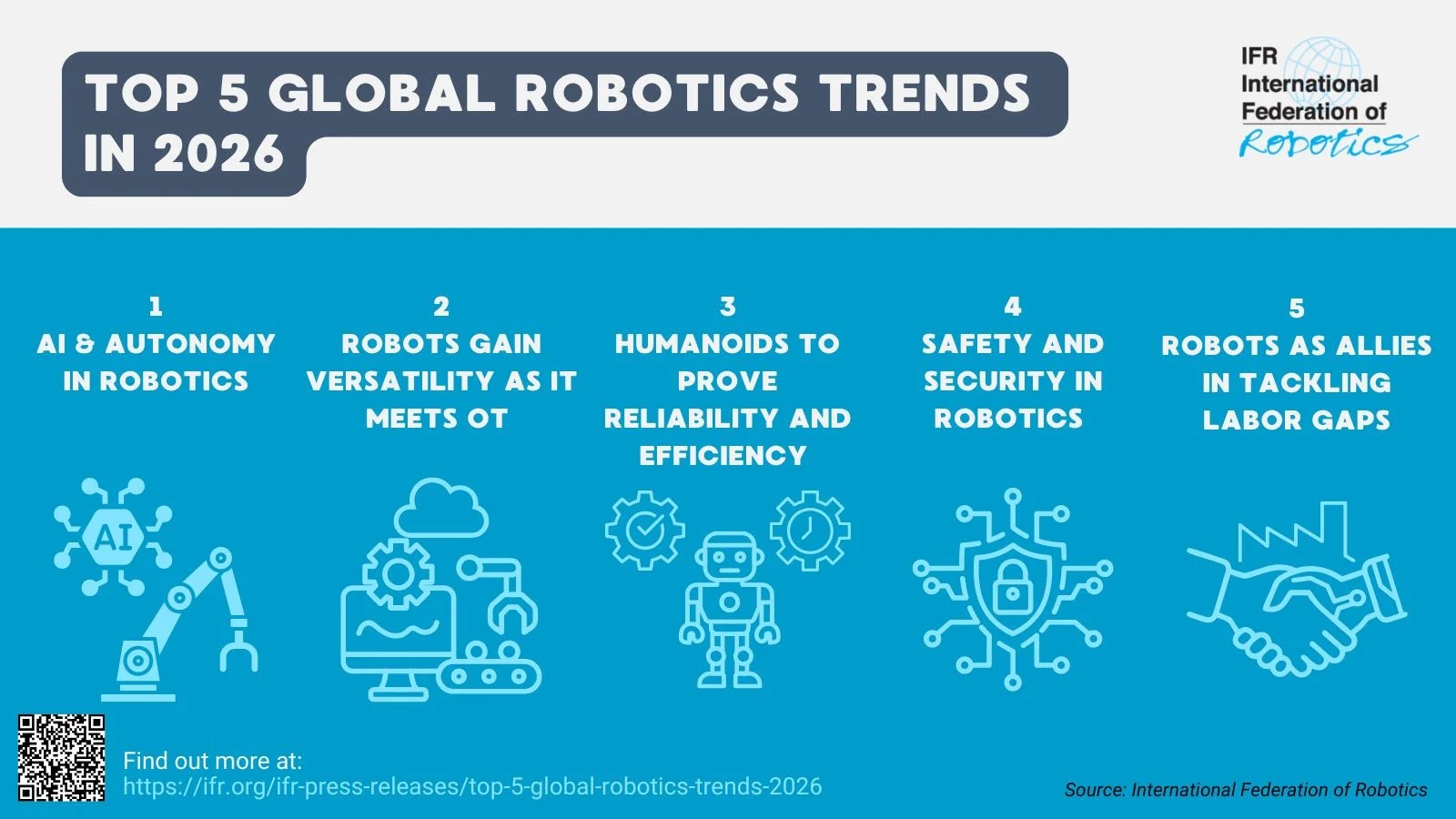
The global market for industrial robot installations has climbed to a record $16.7 billion, reflecting accelerating adoption as manufacturers confront labor shortages, rising complexity, and the need for more flexible automation, according to the International Federation of Robotics. Looking toward 2026, the IFR identifies a set of technology and market shifts that are reshaping how robots are designed, deployed, and governed across industrial and service environments.
AI & Autonomy in Robotics
At the center of those shifts is the rapid expansion of artificial intelligence in robotics, particularly systems that enable higher levels of autonomy. Analytical AI is increasingly used to process large volumes of operational data, allowing robots to anticipate failures, optimize routes, and allocate resources without constant human intervention. Generative AI is extending those capabilities by enabling robots to learn new tasks through simulation, generate training data, and respond to natural-language and vision-based commands. The federation points to the emergence of agentic AI—combining structured decision-making with adaptive learning—as a critical step toward robots that can operate independently in complex, real-world settings.
IT Meets OT
Demand is also rising for robots that can perform a broader range of tasks, driven by the convergence of information technology and operational technology. By linking data-processing systems with physical control systems, manufacturers are enabling real-time data exchange, advanced analytics, and tighter automation loops, IFR pointed out. This integration, a core element of digital enterprise strategies, is breaking down traditional silos between software and machinery and increasing the versatility of robotic systems on factory floors and in logistics operations.
Humanoids to Prove Reliability and Efficiency
Humanoid robots represent another area of growing focus, particularly for environments originally designed for people. After years of prototyping, companies are beginning to test humanoids in industrial settings such as automotive manufacturing, warehousing, and assembly. Commercial success will depend on whether these systems can meet established industrial benchmarks for reliability, energy efficiency, maintenance costs, and safety, according to IFR. To compete with conventional automation, humanoids must demonstrate consistent performance, comply with industry standards, and deliver productivity gains that justify their deployment.
Safety and Security
As robots move closer to humans and become more autonomous, safety and security concerns are intensifying. AI-driven behavior complicates testing, validation, and oversight, increasing the need for rigorous certification and clear liability frameworks. The IFR highlights growing cybersecurity risks as robots connect to cloud platforms and enterprise networks, exposing production systems to potential intrusion or manipulation. At the same time, expanded use of sensors raises questions about data handling, while opaque AI models complicate accountability when systems behave unpredictably.
Adressing Labor Gaps
Underlying many of these trends is a tightening global labor market. Employers across industries are struggling to fill skilled positions, pushing automation to the forefront as a practical response. The IFR emphasizes that successful adoption depends on integrating robots alongside human workers, using automation to relieve routine tasks while supporting reskilling and new career paths. As companies and governments invest in training programs, robots are increasingly positioned as tools to sustain productivity and workforce participation in an economy shaped by automation.
Image credit: IFR