Insider Brief
- Ant Group has open-sourced LingBot-VLA, a vision-language-action model developed by its embodied AI unit Robbyant, aimed at reducing the cost and complexity of deploying embodied AI across different robot types.
- LingBot-VLA has been adapted to robots from Galaxea Dynamics and AgileX Robotics and outperformed peer models on the GM-100 real-robot and RoboTwin 2.0 simulation benchmarks.
- The model was pre-trained on more than 20,000 hours of real-world interaction data, delivers 1.5x to 2.8x faster training than comparable frameworks.
China’s Ant Group said it has open-sourced a new vision-language-action model that is designed to be a “universal brain” aimed at reducing the cost and complexity of deploying embodied AI systems across different types of robots.
The model, called LingBot-VLA, was developed by Robbyant, Ant Group’s embodied intelligence unit, and is intended to function as a shared control layer that can be adapted to multiple robot platforms with limited retraining, according to Ant Group.
The company said the release is designed to address one of the core constraints in real-world robotics: the difficulty of transferring AI models across machines with different physical structures, sensors, and operating environments.
“For embodied intelligence to achieve large-scale adoption, we need highly capable and cost-effective foundation models that work reliably on real hardware,” CEO of Robbyant Zhu Xing said in the announcement: “With LingBot-VLA, we aim to push the limits of reusable, verifiable, and scalable embodied AI for real-world deployment. Our goal is to accelerate the integration of AI into the physical world so it can serve everyone sooner.”
Ant Group said LingBot-VLA has already been adapted to robots produced by manufacturers including Galaxea Dynamics and AgileX Robotic, suggesting that a single model can operate across different mechanical configurations. The company characterized this as evidence of cross-morphology transfer, a longstanding challenge in embodied AI research.
Performance testing was conducted using the GM-100 benchmark, an open evaluation suite developed by Shanghai Jiao Tong University that includes 100 real-world manipulation and interaction tasks. Ant Group said LingBot-VLA achieved higher task completion rates than other models tested across three physical robot platforms. The company also reported that adding depth information improved spatial reasoning performance and raised overall task success rates on the benchmark.
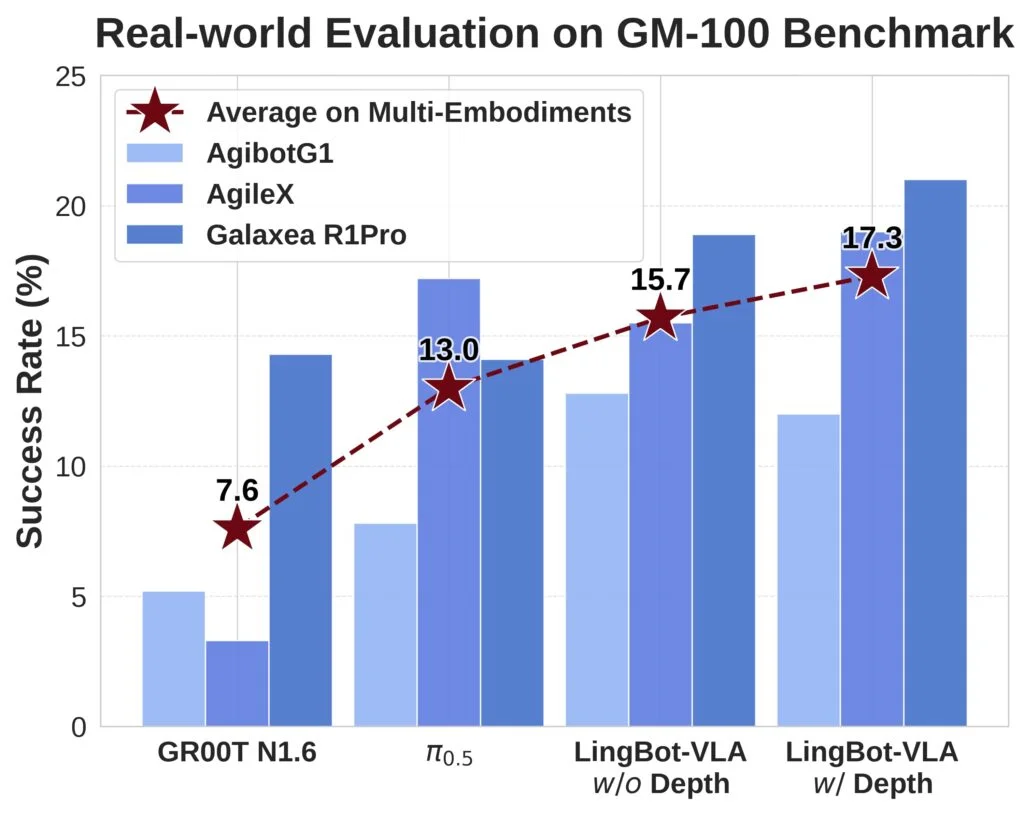
Additional testing was carried out in simulation using the RoboTwin 2.0 benchmark, which introduces environmental variation such as lighting changes, clutter, and positional noise. Ant Group said the model’s internal alignment mechanism allowed it to integrate depth data more effectively under these conditions, producing higher success rates in simulated tasks designed to stress robustness rather than precision.
Ant Group said the release targets persistent inefficiencies in embodied AI development, where models must often be retrained and retuned for each robot or environment, limiting reuse and driving up deployment costs. LingBot-VLA was pre-trained on more than 20,000 hours of real-world interaction data across nine dual-arm robot configurations, which Ant Group said enables a single core model to operate across single-arm, dual-arm, and humanoid robots with consistent performance.
The company said the system also improves efficiency, delivering 1.5x to 2.8x faster training than alternative frameworks and reducing compute needs and development time. Unlike many research releases, the open-source package includes a production-ready software stack that covers data processing, fine-tuning, and automated evaluation, and is intended to support commercial deployment rather than academic testing.
Ant Group described LingBot-VLA as its first open-source embodied AI model and positioned it within its broader InclusionAI initiative. The announcement coincided with Robbyant’s “Evolution of Embodied AI Week,” which also introduced LingBot-Depth, a depth-perception model designed to improve real-world robustness when paired with LingBot-VLA. Ant Group said the release is aimed at developers building deployable robotic systems, with Robbyant serving as the internal lead, and has made the code, documentation, and model weights publicly available.






