Insider Brief
- Chai Discovery has launched Chai-1, an AI model that predicts molecular structures and interactions, offering applications in drug discovery and beyond.
- Chai-1’s multi-modal capabilities allow it to model proteins, small molecules, and nucleic acids, outperforming industry leaders in tasks like protein-ligand interactions and multimer structure prediction.
- While Chai-1 faces some limitations, such as challenges with predicting protein-protein complexes, its open-source availability encourages collaboration, aiming to accelerate advancements in molecular biology and drug development.
Chai Discovery announced on its website that the team has launched Chai-1, a sophisticated artificial intelligence (AI) model designed to predict molecular structures that could have a significant impact on drug discovery and related fields.
Built by a small, technically adept team that combines the worlds of machine learning (ML), life sciences and computer science, Chai-1 offers a new approach to modeling the interactions of proteins, small molecules, DNA and RNA. The model is being hailed as a promising tool for advancing biological research, and it is now freely accessible via a web interface for commercial and non-commercial use.
The Technology Behind Chai-1
Chai-1 is a multi-modal foundation model, meaning it can handle different types of biological data and interactions. The model’s capabilities are broad, ranging from predicting how proteins fold to determining how small molecules bind to proteins, tasks crucial for drug discovery. Chai-1’s performance is notable for its versatility—it can process data in single-sequence mode without relying on multiple sequence alignments (MSAs), a common requirement for many existing protein prediction tools. This allows the model to make accurate predictions with less data, making it particularly useful in situations where comprehensive datasets are not available.
One of the features of Chai-1 that is drawing a lot of attention is its ability to predict the structure of multimers, or complexes formed when multiple proteins interact. According to the company, the model achieves a 69.8% accuracy rate on multimer structure prediction, surpassing the MSA-based AlphaFold Multimer, which scores 67.7%. The ability to make these predictions without extensive sequence data sets Chai-1 apart from its competitors and marks a significant advance in modeling protein interactions.
Chai-1 has also demonstrated strong results in protein-ligand interaction tasks, a key challenge in drug discovery. When tested on the PoseBusters benchmark, which measures how well models predict how small molecules (ligands) bind to proteins, Chai-1 achieved a 77% success rate—slightly outperforming AlphaFold3, one of the industry’s leading models. This makes Chai-1 a valuable tool for pharmaceutical companies looking to identify potential drug candidates more efficiently.
What Are Chai-1’s Practical Uses?
Chai Discovery’s technology, particularly the Chai-1 model, is likely to focus on conditions where molecular interactions play a critical role in treatment development. This includes cancer, where the ability to model protein-ligand interactions could accelerate the identification of new drug candidates that target specific cancer cells. Additionally, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, which involve complex immune system interactions, could benefit from the model’s predictive capabilities in antibody engineering.
Another practical application is in infectious diseases, where Chai-1’s ability to predict RNA and DNA interactions could be useful for developing treatments that target viral genetic material, including those for diseases like HIV and emerging viruses such as SARS-CoV-2. With its multi-modal capabilities, Chai-1 could also aid in designing RNA-based therapies, a rapidly growing area of interest in medical research. These treatments, which rely on accurately predicting nucleic acid structures, could address a variety of genetic disorders, offering a personalized approach to medicine.
Applications in Drug Discovery and Beyond
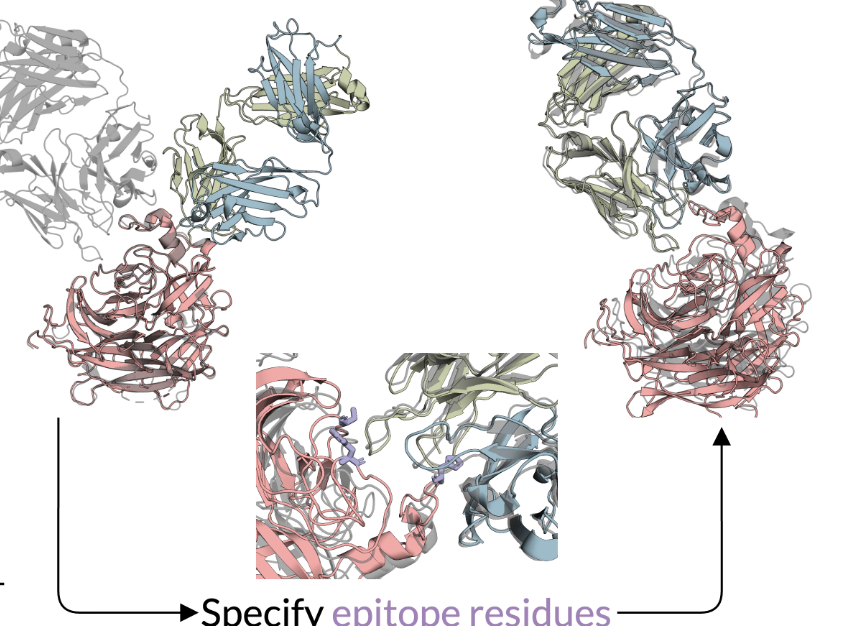
For investors, Chai Discovery is positioned as a powerful resource for the pharmaceutical industry. With its ability to predict the complex interactions between biomolecules, Chai-1 can assist researchers in identifying promising drug candidates and optimizing existing drugs. The model is particularly useful in areas like antibody engineering, where it can enhance predictions by incorporating lab-derived experimental data, such as epitope mapping. This ability to integrate real-world data into the model’s predictions makes it a flexible tool for drug development.
In addition to its immediate applications in drug discovery, Chai-1 could prove valuable in other areas of biological research. The model’s capacity to predict the structure of nucleic acids, for example, could be helpful in studying RNA-based therapies or developing treatments that target genetic material. Chai-1’s multi-modal capabilities make it adaptable to a wide range of tasks, which could lead to applications that extend beyond the pharmaceutical industry, including fields like agriculture and environmental science.
Chai Discovery’s Goals as a ‘Rebel Alliance’
Chai Discovery was founded by a team with deep expertise in both machine learning and biology, including individuals with experience at companies like OpenAI, Meta and Google X. The team’s vision is to transform biology from a scientific discipline into an engineering problem that can be systematically addressed using AI.
The startup has already attracted numerous investors and partners, including of Dimension, Thrive Capital, OpenAI, Conviction, Neo and Amplify Partners. A combination of talent and ambition is part of the reason Chai Discovery is attracting big name investors, according to one of those investors.
In a post on why the firm invested in the startup, Zavain Darr, founder and managing partner of Dimension, writes : “Chai Discovery is founded by a small, extremely ambitious, technically polymathic team of ML, life science, and computer science practitioners. My cofounders, Nan and Adam, and I, have all closely tracked the work of Joshua Meier – a Chai Discovery founder, since his days at Meta and OpenAI in 2019.”
According to Chai Discovery, the launch of Chai-1 represents just the beginning of their efforts to develop AI models that can predict and reprogram biochemical interactions, which are the foundation of life itself.
Chai-1 is the result of several months of intense development, and the company has open-sourced the model to encourage collaboration and innovation within the scientific community.
Darr writes: “Stunningly, in just a few months, Chai Discovery has brought Chai-1 to parity or supremacy over the existing, long standing and financially well coffered incumbents in industry. As part of today’s launch this ‘rebel alliance’ is open sourcing their work. I’m proud that the team is both contributing to open science, but also not resting on the laurels of a snapshot of any single model at any moment in time. Given the continued acceleration and rapid maturation of fundamental ML applied to the current phase shift of “transforming biology from science into engineering” we’re steadfast believers that the long term winning strategy necessitates transparency and open experimentation. For today’s biotech practitioners, there’s inevitably translatable drug discovery value, here for free, at your finger tips.”
Researchers can access the model for free through a web interface, and the underlying code and model weights are available for non-commercial use via GitHub. This decision to open-source the model aligns with the company’s philosophy of transparency and collaboration, which they believe will accelerate the pace of discovery in the field of biology.
Limitations and Challenges
While Chai-1 offers several advantages over existing molecular prediction models, the team does list some limitations. One of the primary challenges with Chai-1 is that, while it can predict the structures of individual protein chains with high accuracy, it sometimes struggles to accurately place these chains in relation to one another when they form larger complexes. This limitation can affect the model’s performance in predicting the interactions between multiple proteins, a critical task in drug discovery.
Chai-1 can also be highly sensitive to modifications in the molecules it predicts. For example, the model may produce significantly different predictions if certain residues in a protein are modified or replaced with their standard analogs. This sensitivity can be a drawback when dealing with modified proteins, which are common in biological systems.
Chai Discovery acknowledges these limitations and is using those limits to actively guide improvements to the model’s performance. The company has stated that future versions of Chai-1 will incorporate additional features, such as better handling of modified residues and improved accuracy in predicting protein-protein interactions.
The Road Ahead
Looking forward, Chai Discovery has ambitious plans to continue developing AI models that address fundamental questions in biology. The team envisions a future where AI models like Chai-1 can not only predict how molecules interact but also design new molecules with specific properties. This shift from prediction to design could have profound implications for drug discovery, synthetic biology, and other fields that rely on understanding and manipulating the molecular machinery of life.
Chai-1 is a promising tool in the field of molecular prediction, offering both flexibility and precision in modeling complex biological systems. While it faces some limitations, its open-source nature and strong performance make it a valuable resource for researchers and pharmaceutical companies alike. As the technology continues to evolve, Chai Discovery aims to push the boundaries of what is possible in molecular biology, with the ultimate goal of transforming how we approach the study of life itself.