Insider Brief
- AI companion robots will likely continue to play a complementary role in elderly care, offering emotional support, reducing loneliness, and assisting with routine tasks, but they cannot replace human caregivers and remain limited by ethical, cultural, and practical challenges.
- Countries including Japan, China, Sweden, South Korea, and the U.S. are piloting robots such as PARO, ElliQ, Buddy, Hyodol, and animatronic pets, showing how these devices are being integrated into real-world care environments to support aging populations.
- While studies show benefits like easing caregiver workload and improving patient engagement, concerns persist over privacy, job displacement, complexity of use, and robots’ inability to replicate human empathy, leaving the future of widespread adoption uncertain.
The world’s population is aging at an unprecedented rate. According to the World Health Organization, the number of people aged 60 and above is expected to grow from about 1.1 billion in 2023 to 1.4 billion by 2030 amd 2.. This demographic shift is creating immense pressure on healthcare and elder care systems. Many countries face severe caregiver shortages – a Global Coalition on Aging report projected a shortage of 13.5 million care workers by 2040 across OECD countries.
Governments and companies worldwide are investing in robotics and artificial intelligence to help care for seniors. The most prevelant is the AI companion.
How are AI Companions Robots Used in Senior Care?
AI companion robots – machines designed to provide assistance or companionship to older adults – have been deployed across the globe for decades.
Japan has been a pioneer in deploying eldercare robots, with government subsidizing beginning in 2015. Private care operators report using doll-sized robots to lead songs and games, while others deploy sleep-monitoring sensors. Waseda University’s AIREC has introduced a humanoid robot, weighing 150 kg, can turn bedridden patients to prevent sores and even help cook meals, moving beyond mere companionship, according to Reuters. Though prototypes cost around $67,000, developers expect adoption by 2030.
PARO Therapeutic Seal, from AIST in Japan, is robotic seal used as pet therapy for dementia patients that was first launched in 2004. PARO responds to touch and sound, providing calming companionship.
It’s not just Japan, countries around the world, robotic companions are moving into real elder care environments.
ElliQ, by Intuition Robotics, is a tabletop social robot designed as a proactive AI companion for older adults. In a New York State pilot with 800 seniors, ElliQ users reported a 95% reduction in loneliness. The device initiates conversations, reminds seniors about medication, and even uses generative AI for natural interactions.
Buddy, by Blue Frog Robotics, is a mobile companion robot that reminds elders about schedules, connects them to family via video, and provides entertainment and South Korea, the Hyodol robot converses in Korean and recognize emotions with the appearance and speech patterns of a 7-year-old child.
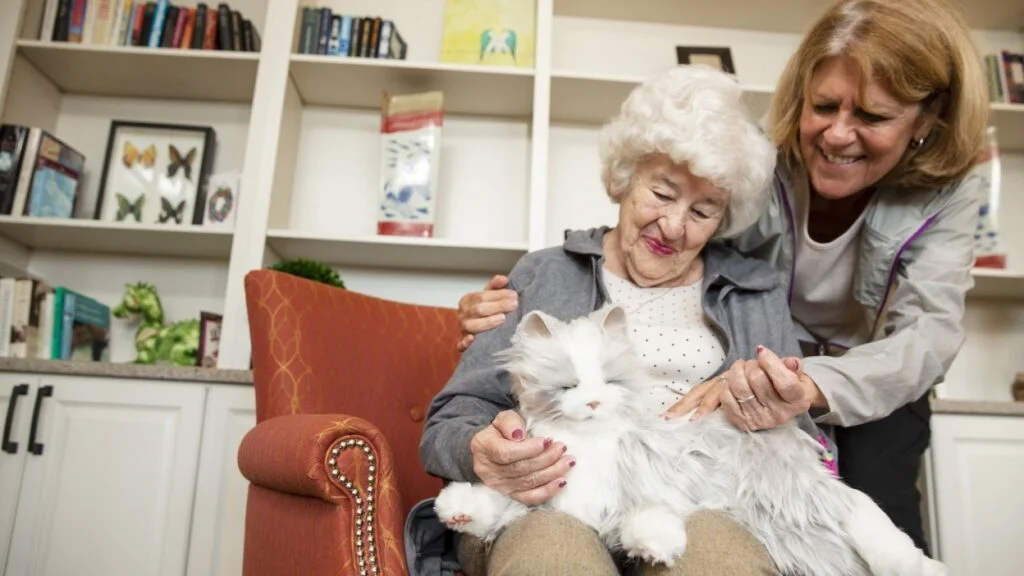
In Sweden, 52% of municipalities use robotic cats and dogs in elder care homes. A study by Linköping University noted caregivers report residents who had been non-verbal began speaking to robot pets, and anxious patients became calmer. Ageless Innovation is using animatronic cats, dogs, and birds to combat loneliness among seniors, with programs distributing the companion pets in hospice care, veterans’ facilities, and most recently to residents 60 and older in three Washington, D.C. wards, the company noted.

China recently launched a national pilot program to accelerate robot use in elder care. The Chinese Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and the Ministry of Civil Affairs are deploying robots in homes, community centers, and institutions to assist with disabilities, cognitive issues, and daily tasks, China Daily reports. Over the next three years, China plans to test at least 200 robots and set industry standards. With China’s population aged 60 and above already surpassing 300 million and expected to exceed 400 million by 2035, the program is designed to prepare for the country’s rapidly aging society.
What are the Benefits and Criticisms of Robots in Elderly Care
A 2025 study “Social Robots in Elderly Care: A Scoping Review of Caregiver Perspectives” reviewed 31 studies published between 2015 and 2024 on caregivers’ perceptions of social robots in elderly care. Overall, caregivers expressed cautious optimism, supporting the use of robots as complementary aids that could reduce workload, support communication, and assist with routine tasks. They valued features such as ease of use, reliability, adaptability, personalization, and the ability to provide social and cognitive engagement for older adults. The study found benefits and concerns from caregivers that include:
Benefits
- Reduce caregiver workload and physical strain by handling routine or demanding tasks, improving overall job satisfaction.
- Enhance quality of care when used as complementary aids, particularly by supporting communication, engagement, and reducing loneliness among elderly patients.
- Provide cognitive and emotional support, especially for patients with dementia, fostering positive caregiver-patient interactions.
- Offer valued features such as user-friendliness, adaptability, personalization, reliability, and safety, which make integration into daily care routines easier.
Concerns and Limitations
- Ethical concerns around privacy, autonomy, stereotypes, and the risk of dehumanizing care.
- Potential fears of job displacement and reduced human contact in eldercare settings.
- Complexity of setup and training requirements may initially create additional burdens or anxiety for caregivers.
- Limited ability to replicate nuanced human interactions or provide the depth of emotional support required.
- Cultural and institutional differences affect acceptance, and there are still gaps in research on long-term psychological and professional impacts.
The review concluded that robots are most successful when they enhance rather than replace human caregiving, with ethical design principles ensuring dignity, privacy, and autonomy for the elderly. Integration requires user-friendly interfaces and seamless incorporation into care routines. Research gaps remain around long-term impacts on caregivers’ mental health, job satisfaction, and professional roles, underscoring the need for further longitudinal and context-specific studies.
What is the Future of Companion AI Robots?
As AI and Robotics Rapidly Advance, whether they will play more of a role in senior care remains to be seen. Despite development of these devices, at this time they still require human time and effort in real-world settings.
Japan has invested heavily in care robots like Robear, Pepper, and Paro to address its rapidly aging population and caregiver shortages, but real-world adoption remains limited, a 2023 MIT study found. Ethnographic studies show that while these robots can provide entertainment, therapy, or physical assistance, they often create extra work for caregivers, require constant supervision, and fail to deliver on promises of reducing labor.
MIT noted that surveys reveal that only a small fraction of care facilities and home caregivers actually use robots, and many devices end up stored away after brief trials. Analysts argue that the push for robotic care reflects techno-solutionism and political choices to avoid raising wages or expanding migrant labor, rather than truly improving eldercare. Ultimately, while robots can complement human work, care remains a deeply social and relational task, best addressed through better pay, working conditions, and broader social support rather than expensive technological fixes.
.