Insider Brief
- EvolutionaryScale has successfully closed a seed funding round of over $142 million.
- Nat Friedman and Daniel Gross led the round, with significant contributions from Lux Capital, Amazon, NVentures, and other angel investors.
- EvolutionaryScale also introduced its latest AI model, ESM3, which simulates 500 million years of evolutionary processes to generate new protein.
EvolutionaryScale, an emerging AI research lab focused on biology, has successfully closed a seed funding round of over $142 million, according to a company statement and blog post. They also published a research paper on the tool, which will be added to a pre-print server.
The round was led by Nat Friedman and Daniel Gross, with significant contributions from Lux Capital, Amazon, NVentures, and other angel investors. This investment will enable the company to expand the capabilities of its AI models for protein design.
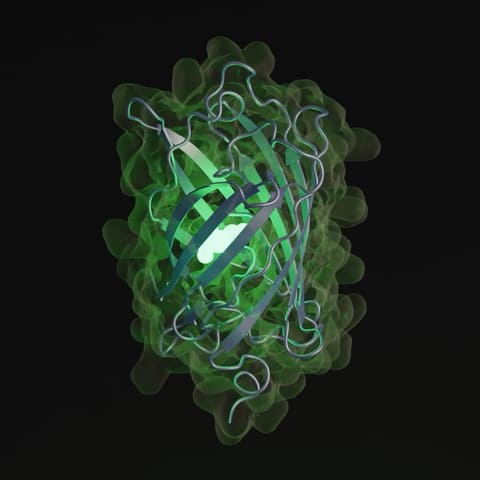
EvolutionaryScale has introduced its latest AI model, ESM3, which simulates 500 million years of evolutionary processes to generate new proteins. This includes the creation of a novel Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP), a task that would take millions of years to occur naturally. ESM3 was trained on 2.78 billion proteins with 1 trillion teraflops, making it one of the most computationally intensive models in biology.
ESM3 allows scientists to create new proteins through interactive prompting, supporting applications in drug discovery, materials science, and carbon capture. Alexander Rives, co-founder and chief scientist at EvolutionaryScale, said: “ESM3 represents a step towards a future where biology can be engineered like other fields such as computer science and mechanical engineering. We’ve been working on this for a long time, and we’re excited to share it with the scientific community and see what they do with it.”
The company has detailed this development in a scientific preprint and released an open version of the model for the scientific community. ESM3 not only understands but also generates proteins by reasoning over their sequence, structure, and function, potentially speeding up discoveries in various fields, from developing new cancer treatments to designing proteins for carbon capture.
GFP, known for its glowing properties in jellyfish and coral, is an essential tool in molecular biology for visualizing molecules inside cells. The new GFP variant generated by ESM3 highlights the model’s potential in biological research.
In collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and NVIDIA, EvolutionaryScale aims to make ESM3 accessible to a wider range of researchers and institutions, according to the statement. This includes an API for closed beta and optimization for training and inference performance through NVIDIA’s BioNeMo and AI Enterprise software. The full ESM3 model family will be available to hundreds of thousands of researchers and major pharmaceutical companies using AWS’s generative AI and health services.
For further information on ESM3 and to access the preprint paper, visit the EvolutionaryScale blog at https://www.evolutionaryscale.ai/blog/esm3-release.